Editorial for Baltic OI '19 P4 - Tom's Kitchen
Submitting an official solution before solving the problem yourself is a bannable offence.
Subtask 1 was intended to permit simple case-analysis based solutions.
Subtask 2 was intended to permit brute force search solutions.
Subtask 3 was a reduction to a standard Dynamic Programming problem (commonly stated as: you have certain coins, find if you can pay exactly amount of money with them).
Subtask 4 was intended to permit task-specific but suboptimal Dynamic Programming solutions.
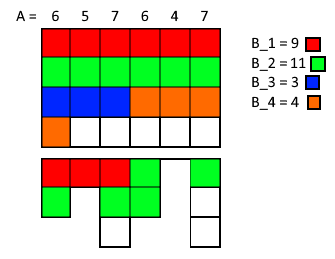
The full solution uses Dynamic Programming. Let us mentally reorder the hours spent on each meal such that for the first hours, all chefs are different. This way we can visualize these
hours forming an
"diversity box", with all "non-diverse hours" coming afterwards (as shown in the figure above). Now let's make the following observations:
- Each chef can add at most
hour to any column of the "diversity box".
- A chef
can fill the "diversity box" by at most
.
- In a correct solution, the "diversity box" must be filled by an amount of at least
.
- Suppose you have decided to hire chefs for a total of
hours. Then it's optimal to hire such set of chefs that the "diversity box" is filled as much as possible (perhaps even overfilled).
Now let be the maximum amount we can fill the "diversity box" by picking a subset of chefs
such that they are hired for a total of
hours. Now let us notice that for the value
there are two possibilities:
- The maximal subset contains chef
. Thus the other chefs in this subset form a maximal solution for
(otherwise we could pick a better subset). Thus
.
- The maximal subset doesn't contain chef
. Thus this subset also forms a maximal solution for
(a better solution to
would contradict the maximality of this subset). Thus
.
Now we simply need to consider the two cases and see which gives us a better solution. Thus . For performing the dynamic programming computation, we can initialize
to
and every other
to
. Note that once we have computed
we don't care about
anymore, so we can optimize memory consumption. The answer will be minimum non-negative
such that
.
Credits
- Task: Bernhard Linn Hilmarsson (Iceland)
- Solutions and tests: Oliver-Matis Lill, Andres Unt (Estonia)
Comments